Hook: Did you know that over 30% of men over 40 experience low testosterone—and that what you eat is one of the most influential factors? Unlocking the power of the right diet for testosterone production can transform your energy levels, mood, and overall well-being. This comprehensive guide reveals the science, the foods, and the strategies you need to naturally boost testosterone starting today.
Revealing the Shocking Connection: Diet for Testosterone Production and Your Health
The relationship between your daily dietary pattern and testosterone levels is profound. What you consume impacts not only your immediate energy but also the delicate balance of hormones—including testosterone. Recent studies point to nutritional choices as both a risk factor for testosterone deficiency and a pivotal way to increase testosterone naturally. From optimizing protein intake to ensuring you get the right balance of healthy fats, each element of your diet contributes to your body's ability to produce and maintain this essential sex hormone. For healthy men and those at risk of low testosterone, understanding and leveraging nutrition is essential for maintaining muscle mass, vigor, and overall hormonal health. The following sections will break down the science, practical steps, and recommended foods you need to know for the best diet for testosterone production.
Startling Facts: The Prevalence of Testosterone Deficiency and Its Link to Diet
Recent epidemiological research makes it clear that testosterone deficiency is becoming increasingly common. Over 30% of men above the age of 40 now experience low testosterone, leading to issues that range from decreased muscle mass and mood changes to diminished libido and energy. This isn’t just a matter of aging; clinical data reveals that dietary habits—especially high intakes of processed foods, excess sugar, and unhealthy fats—play a direct role in lowering testosterone levels. Conversely, populations with a nutrient-rich, balanced diet have significantly higher levels of testosterone and better overall health outcomes. It's important to note that while genetics and age matter, day-to-day food choices are powerful determinants of hormonal balance, capable of either improving or sabotaging total testosterone and free testosterone production.
"Did you know that over 30% of men over 40 experience low testosterone, and diet is a major contributing factor?"

What You’ll Learn About Diet for Testosterone Production
The critical nutrients that influence testosterone levels
Specific foods proven to boost testosterone production
How to structure your diet for optimal testosterone health
Natural ways to counteract lower testosterone
Why natural strategies outperform synthetic solutions
Understanding Testosterone Deficiency and the Role of Diet for Testosterone Production
What Is Testosterone Deficiency?
Testosterone deficiency, also known as hypogonadism, refers to the body's inability to produce adequate levels of this essential sex hormone. Testosterone is critical for maintaining muscle mass, bone density, sex drive, energy, and mood in men and, to a lesser degree, women. Symptoms often manifest subtly—chronic fatigue, increased body fat, loss of muscle, and even mild depression. It’s important to note that poor dietary habits can contribute heavily to this state. A lack of key nutrients like zinc, deficiency in healthy fats, and erratic protein intake have all been connected to a greater risk of low testosterone. By understanding these triggers and taking proactive steps with a balanced diet, you can support healthy testosterone levels and offset some of the negative effects associated with aging and modern lifestyles.

How Diet Directly Affects Testosterone Levels
Your diet affects testosterone levels through multiple pathways. For instance, inadequate protein intake can compromise muscle repair and reduce the building blocks necessary for hormone synthesis. A diet full of processed foods and trans fats is directly linked with increased body fat and insulin resistance, both of which have a negative effect on testosterone. Healthy fats, particularly those from fatty fish and nuts, support hormone production by supplying cholesterol, a precursor required for testosterone synthesis. Furthermore, sufficient intake of micronutrients like zinc, magnesium, and vitamin D is essential for maintaining optimal hormone levels. Dietary choices that favor whole, unprocessed foods and balance carbs, protein, and healthy fats can dramatically boost testosterone and reduce the risk of hormonal imbalances.
Symptoms of Low Testosterone and Dietary Links
Recognizing low testosterone early is key to reversing its effects with dietary adjustments. Common symptoms include reduced muscle mass, increased abdominal fat, low energy, irritability, and reduced libido. Many of these symptoms are aggravated by diets high in sugar, processed foods, and refined grains, which can further lower testosterone levels and disrupt other hormone balances. Conversely, studies suggest that individuals consuming a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, green vegetables, and healthy fats often experience improvements in both mood and physical stamina as their testosterone levels stabilize.
Key Nutritional Foundations in a Diet for Testosterone Production
Protein Intake: Building Blocks for Boosting Testosterone
Protein intake is foundational for boosting testosterone and supporting muscle repair. Dietary proteins supply essential amino acids that the body uses to build muscle and produce hormones. A shortage of dietary protein can lead to reduced production of sex hormones, including testosterone, and a loss of muscle mass over time. Consuming high-quality protein sources such as lean meats, eggs, and dairy supports not only serum testosterone levels but also overall metabolic health. It’s recommended that healthy men aiming to optimize testosterone intake at least 1.0-1.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day, varying with age, activity, and specific health goals.
"Adequate protein intake is essential for maintaining healthy testosterone levels and supporting muscle repair." — Nutrition Expert
Healthy Fats and Their Impact on Testosterone Level
Healthy fats, including monounsaturated and omega-3 fatty acids, play a crucial role in supporting testosterone production. Unlike saturated and trans fats commonly found in processed foods—which can lower testosterone—healthy fats are necessary for hormone synthesis at every level. Fatty fish like salmon and sardines, avocados, nuts, and seeds provide an excellent source of these beneficial fats. Diets excessively low in fat can harm hormone generation, while a well-balanced intake can dramatically increase testosterone levels and reduce inflammation. The following table compares fat types and their effects on testosterone.
Comparison of Fat Types and Their Effects on Testosterone Levels | ||
Fat Type |
Examples |
Effect on Testosterone |
|---|---|---|
Monounsaturated Fats |
Olives, avocados, nuts |
Boost testosterone production |
Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fats |
Fatty fish, flaxseeds, walnuts |
Increase testosterone, reduce inflammation |
Saturated Fats |
Butter, cheese, red meat |
Neutral to slightly positive in moderation |
Trans Fats |
Fried, processed, baked goods |
Negative effect, lower testosterone |
Carbohydrate Choice: How Carbs Can Affect Testosterone
Carbohydrate intake also plays an important role in hormone health. Excess refined sugar and simple carbohydrates can spike insulin, which in turn may lower testosterone. However, the right kinds of carbs—like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables—provide slow-release energy and fiber that support metabolic stability and help maintain a healthy weight. For optimal testosterone health, focus on whole-food carbohydrates while minimizing processed and sugary options. When combined with balanced protein and fats, dietary carbs can help regulate stress hormones, blunt insulin spikes, and ensure that testosterone production remains robust.

Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals Driving Testosterone Production
The role of micronutrients should not be understated in crafting an effective diet for testosterone production. Deficiencies in zinc, vitamin D, and magnesium are closely associated with low testosterone. These vitamins and minerals act as co-factors in the biological processes responsible for hormone synthesis, enzyme activity, and overall endocrine health. Frequently found in nuts, seeds, green vegetables, lean meats, and dairy, these micronutrients are best absorbed from whole foods. In some cases, considering a zinc supplement or a vitamin D supplement may be warranted, especially if dietary intake or sun exposure is limited. The core micronutrients for boosting testosterone are:
Zinc
Vitamin D
Magnesium
B Vitamins
Top Foods to Include in a Diet for Testosterone Production
Fatty Fish: Omega-3 Powerhouses for Increasing Testosterone
Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines are among the most potent foods for increasing testosterone naturally. Rich in omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, these fish not only reduce systemic inflammation but also directly support hormone synthesis. Including two to three servings of fatty fish per week can help elevate testosterone levels while providing additional cardiovascular and brain health benefits. In addition to omega-3s, these fish are also excellent sources of vitamin D and protein, making them an all-around superior choice for anyone seeking to improve hormone health through diet.

Green Vegetables: Essential Micronutrients for Boost Testosterone
Green vegetables—especially spinach, broccoli, and kale—are nutritional powerhouses packed with magnesium, vitamin C, folate, and essential antioxidants. These nutrients play a direct role in reducing inflammation and promoting the efficient production of testosterone. High antioxidant content helps combat oxidative stress, which is known to lower testosterone and disrupt hormone balance. Regularly incorporating green vegetables into your meals ensures your body is equipped to maintain high testosterone levels and can make a noticeable difference in energy and well-being.
Lean Meats and Eggs: Protein Intake for Optimizing Testosterone Levels
Lean meats such as chicken breast, turkey, and grass-fed beef, along with whole eggs, are top performers when it comes to protein intake and supporting testosterone. The amino acids from these proteins serve as the building blocks not just for muscle mass, but also for sex hormone production. Eggs in particular provide vitamin D and healthy fats that contribute to hormone synthesis, while meats supply heme iron and additional zinc. When consumed as part of a balanced diet, lean meats and eggs help sustain energy, metabolism, and promote a stable hormone profile.
Nuts and Seeds: Healthy Fats to Boost Testosterone
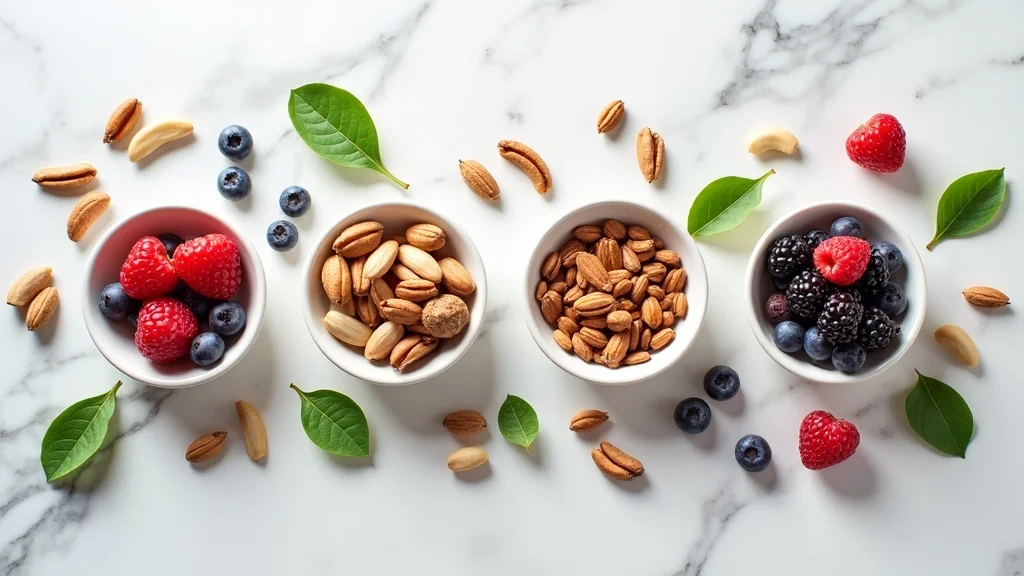
Nuts (such as almonds and walnuts) and seeds (like pumpkin and chia) provide healthy fats, fiber, magnesium, and antioxidants—all crucial for testosterone production. Studies suggest that men who regularly consume nuts and seeds have healthier hormone profiles than those who don’t. The fats found in these foods are predominantly unsaturated and actively contribute to hormone-building cellular processes. In addition, seeds are rich in zinc, a mineral with a direct link to increasing testosterone and averting deficiency symptoms.
Antioxidant-Rich Fruits: Reduce Testosterone-Reducing Oxidative Stress
Fruits rich in antioxidants, such as berries, pomegranates, and citrus, are valuable for minimizing oxidative damage that can reduce testosterone over time. Oxidative stress from pollution, poor diet, or chronic illness has been shown to lower testosterone production. Incorporating a rainbow of fruits not only provides key phytochemicals and fiber but also helps support overall immune strength—facilitating a more robust hormonal system.
Salmon
Spinach
Chicken breast
Pumpkin seeds
Berries

Foods and Habits to Avoid for Lower Testosterone Risk
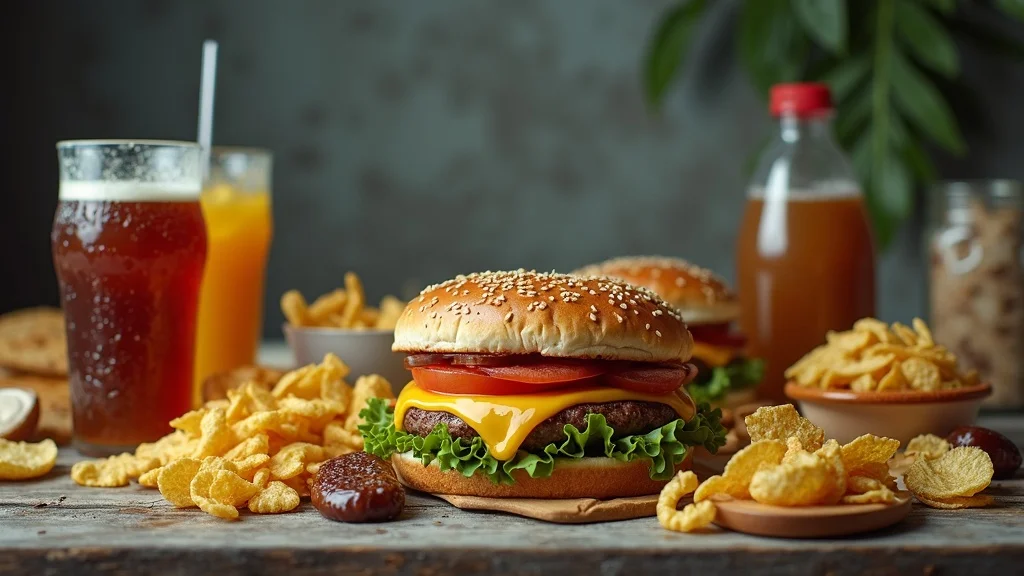
Highly Processed Foods and Their Link to Reduced Testosterone
Highly processed foods—think fast food, frozen meals, and snacks loaded with trans fats and artificial additives—pose a genuine risk to testosterone health. These foods are often high in empty calories and offer little in terms of vital vitamins and minerals while packing a high glycemic load that can spike insulin and lead to weight gain. Evidence connects high intake of processed foods directly to lower testosterone levels, increased inflammation, and disrupted metabolic health. The negative effect of these dietary patterns should not be underestimated; over time, they can significantly reduce testosterone and lead to additional hormonal imbalances.

Alcohol Consumption: How It Can Lower Testosterone Levels
Excessive alcohol intake is another major culprit that can negatively impact testosterone levels. Even moderate drinking has been shown to interfere with testicular function, inhibit testosterone synthesis, and raise estrogen levels. Alcohol also often leads to poor dietary choices, compounding the negative effects. By limiting or avoiding alcohol, especially in conjunction with a whole-food, balanced diet, you can significantly protect your hormonal health and lower your risk of testosterone deficiency.
Excess Sugar Intake: A Hidden Trigger for Low Testosterone
High sugar consumption is strongly linked to increased insulin resistance, obesity, and chronic inflammation—all of which notoriously lower testosterone. Many processed foods, sodas, and desserts contain hidden sugars that can stealthily sabotage your hormone balance. Efforts to limit sugar—choosing whole fruits over desserts, drinking water instead of soda, and reducing processed snack intake—can lead to rapid improvements in not only testosterone levels but overall metabolic health.
How to Create the Best Diet for Testosterone Production: Step-By-Step Guide
Assess your current testosterone levels and dietary habits
Increase testosterone-boosting foods
Limit foods that reduce testosterone
Monitor protein, fat, and carbohydrate ratio
Incorporate recommended vitamins and minerals
Sample Meal Plan for a Week Focused on Testosterone Production
Building your weekly menu around testosterone-friendly foods doesn’t have to be complicated. Focus on whole food sources of protein, heart-healthy fats, and a diversity of vegetables and fruits. Here’s a sample meal plan demonstrating optimal choices for each day.
Meal Plan Table: Day-by-Day Foods to Boost Testosterone and Optimize Hormone Level | ||||
Day |
Breakfast |
Lunch |
Dinner |
Snacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Mon |
3 eggs, spinach, whole grain toast |
Grilled salmon, quinoa, broccoli |
Chicken breast, sweet potatoes, kale salad |
Pumpkin seeds, berries |
Tue |
Greek yogurt, walnuts, berries |
Tuna salad with avocado, mixed greens |
Turkey stir-fry, brown rice, roasted asparagus |
Almonds, citrus slices |
Wed |
Omelet with mushrooms and onions, side of fruit |
Beef steak, spinach salad, sweet potato |
Grilled mackerel, lentils, green beans |
Sunflower seeds, grapes |
Thu |
Overnight oats, chia seeds, banana |
Chicken wrap with whole grain tortilla, peppers |
Baked salmon, wild rice, Brussels sprouts |
Pistachios, apple slices |
Fri |
Boiled eggs, avocado, tomato slices |
Shrimp and spinach salad, quinoa |
Lamb chops, broccoli, carrots |
Mixed nuts, pomegranate seeds |
Sat |
High-protein smoothie (whey, spinach, berries) |
Turkey burger, lettuce wrap, veggies |
Grilled chicken, sweet potato, zucchini |
Pumpkin seeds, pear slices |
Sun |
Cottage cheese, berries, flaxseed |
Salmon bowl (rice, broccoli, carrots) |
Beef stir-fry, brown rice, bok choy |
Almonds, orange slices |

Watch: Dynamic explainer animation reveals how key nutrients, smart food choices, and supportive lifestyle habits work together at the biological level to boost testosterone and optimize your hormone health.
Natural Strategies to Improve Testosterone Production Beyond Food
The Role of Physical Activity and Stress Reduction on Levels of Testosterone
Nutrition is foundational, but physical activity—especially resistance training—also has a significant effect on testosterone levels. Regular weightlifting and high-intensity interval training have been shown to increase testosterone naturally by stimulating hormone production and preserving muscle mass. Equally important are stress reduction techniques, such as mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing, which can help lower cortisol and prevent it from negatively impacting testosterone. Combining a whole-food, testosterone-friendly diet with consistent exercise and proactive stress management offers the most powerful approach for achieving balanced hormone levels.

Sleep Patterns and Their Effect on Testosterone Production
Quality sleep is a non-negotiable part of healthy hormone function. Most testosterone is produced during deep sleep. Chronic sleep deprivation can quickly lead to a drop in testosterone, increased irritability, and a weakened immune system. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, optimizing your sleep environment for comfort, and aiming for at least 7-8 hours per night are among the best ways to support hormone levels—and by extension, every other aspect of health and wellbeing.
Weight resistance training
Mindfulness techniques
Consistent sleep schedule

Natural vs Synthetic: Why Using Natural Testosterone Supplements Are Better
"Natural approaches deliver sustainable results without the side effects of synthetic testosterone replacement."
Research Backing Natural Boosters for Testosterone
Numerous studies support the use of natural testosterone boosters—such as certain herbal supplements, increased vitamin D, and optimized protein intake—for improving hormone levels safely and effectively. Natural approaches are generally safer, with fewer risks and no dependency, unlike synthetic testosterone treatments. When combined with a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle habits, these solutions can help you both reach and sustain optimal testosterone levels.
Common Pitfalls of Synthetic Testosterone Treatments
While synthetic testosterone therapies may offer rapid results, they are associated with a host of possible side effects—from cardiovascular risks to infertility. Long-term use can impair your body’s natural hormone production, creating a dependency. Natural methods, on the other hand, work in harmony with your body’s systems, ensuring that hormonal balance can be achieved and maintained without negative long-term consequences.
Watch: An expert-led review discusses real-world results, favorite recipes, and advanced dietary tips for those looking to maximize testosterone naturally.
People Also Ask About Diet for Testosterone Production
What diet produces the most testosterone?
Answer
The diet that best supports testosterone production is rich in lean proteins (such as grass-fed meats, eggs, and fatty fish), healthy fats (olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds), and plenty of green vegetables like spinach and broccoli. Whole grains, berries, and antioxidant-rich fruits also contribute. Avoiding processed foods, reducing sugar, and moderating alcohol intake are also crucial. This balanced approach covers all the key nutrients proven to boost testosterone levels.
How can I get 1000 testosterone naturally?
Answer
Achieving naturally high testosterone (e.g., around 1000 ng/dL) requires a multifaceted approach: consistently eating a hormone-supportive diet, engaging in regular resistance training, minimizing stress, getting quality sleep, and ensuring adequate intake of key micronutrients like zinc, vitamin D, and magnesium. Some individuals may benefit from specific supplements, but natural lifestyle strategies should always come first.
Does not ejaculating for 7 days increase testosterone?
Answer
While some studies have suggested a temporary spike in testosterone after periods of abstinence, the effect is short-lived and unlikely to have a meaningful long-term impact. Lasting increases in testosterone are better achieved through sustainable changes in diet, exercise, and sleep patterns.
How can I raise my testosterone level quickly?
Answer
Quick improvements in testosterone can be achieved by getting adequate rest, performing intense resistance training, consuming a meal rich in protein and healthy fats, managing stress actively, and ensuring proper hydration. While supplements can help, focusing on foundational diet and lifestyle habits will produce the most consistent and safe results.
FAQs on Diet for Testosterone Production
What is the best protein intake for testosterone?
Do fatty fish really boost testosterone?
Can green vegetables affect testosterone levels?
Which foods reduce testosterone and should be minimized?
How soon can diet changes improve testosterone level?
Key Takeaways on Diet for Testosterone Production
Balanced nutrition is key to maintaining healthy testosterone levels
Certain foods significantly boost testosterone production
Natural approaches should be prioritized over synthetic hormones
Ready to Boost Testosterone? Try This Natural Testosterone Supplement
"Take the next step towards optimal health. Discover our recommended Natural Testosterone Supplement for a safe, natural boost."
Interested in a reliable, natural way to further support your hormone health? Try our recommended Natural Testosterone Supplement and take your results to the next level—backed by science and trusted by healthy men worldwide.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment